Ethos, pathos, and logos play an important role in PR.
Some people need righteous arguments to be persuaded. Some need emotional ones. Others need logical arguments to come around.
But for most of us, a combination of the three is needed.
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three powerful modes of persuasion in public relations.
Here we go:
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Public Relations
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos: Three Modes of Persuasion
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three modes of persuasion recognised since ancient Greece, and they play an essential role in public relations.
“Aristotle’s three modes of rhetorical persuasion are ethos, pathos, and logos, which are based on moral competence, emotional appeal, and reason.”
Source: Sino-US English Teaching 1Lin, W. (2019). Three Modes of Rhetorical Persuasion. Sino-US English Teaching. https://doi.org/10.17265/1539 – 8072⁄2019.03.003

In PR, these three modes of persuasion are often combined to create compelling messages that resonate with the audience on multiple levels. 2Modes of persuasion. (2023, September 27). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modes_of_persuasion
By understanding and applying the principles of ethos, pathos, and logos, PR professionals can craft messages that resonate deeply with their audience, driving action and fostering lasting relationships.
Learn more: Ethos, Pathos, and Logos in Public Relations

THANKS FOR READING.
Need PR help? Hire me here.

PR Resource: Persuasion
Spin Academy | Online PR Courses

Spin’s PR School: Free Persuasion PR Course
Use this free Persuasion PR Course to elevate your public relations game with powerful insights. Drive impact and influence like never before.
Persuasion 101
Advanced Persuasion
Propaganda
Learn more: All Free PR Courses
💡 Subscribe and get a free ebook on how to get better PR.

PR Resource: Amplification Hypothesis
The Amplification Hypothesis
It’s common to find that counterarguments strengthen existing beliefs instead of weakening them.
The harder you attack someone verbally, the more you convince them of their belief, not yours.
The phenomenon is known as the amplification hypothesis, where displaying certainty about an attitude when talking with another person increases and hardens that attitude.
“Across experiments, it is demonstrated that increasing attitude certainty strengthens attitudes (e.g., increases their resistance to persuasion) when attitudes are univalent but weakens attitudes (e.g., decreases their resistance to persuasion) when attitudes are ambivalent. These results are consistent with the amplification hypothesis.“
Source: Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 3Clarkson, J. J., Tormala, Z. L., & Rucker, D. D. (2008). A new look at the consequences of attitude certainty: The amplification hypothesis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, … Continue reading
How does the amplification hypothesis work?
In a threatening situation or emergency, we resort to the primal (fastest) part of the brain and survival instincts (fight, flight and freeze). 4Surviving the Storm: Understanding the Nature of Attacks held at Animal Care Expo, 2011 in Orlando, FL.
Establishing common ground and exhibiting empathy demonstrates a genuine understanding of their perspective, fostering trust and openness to your ideas. Conversely, a strategic mismatch of attitudes can serve as a powerful countermeasure if your objective is to deflect persuasive attempts.
Persuade
To persuade, align your attitude with the target. Otherwise, you will only act to create resistance.
Provoke
To put off a persuader, mismatch their attitudes. When they are logical, be emotional, and vice versa.
Learn more: The Amplification Hypothesis: How To Counter Extreme Positions
PR Resource: Perception Management
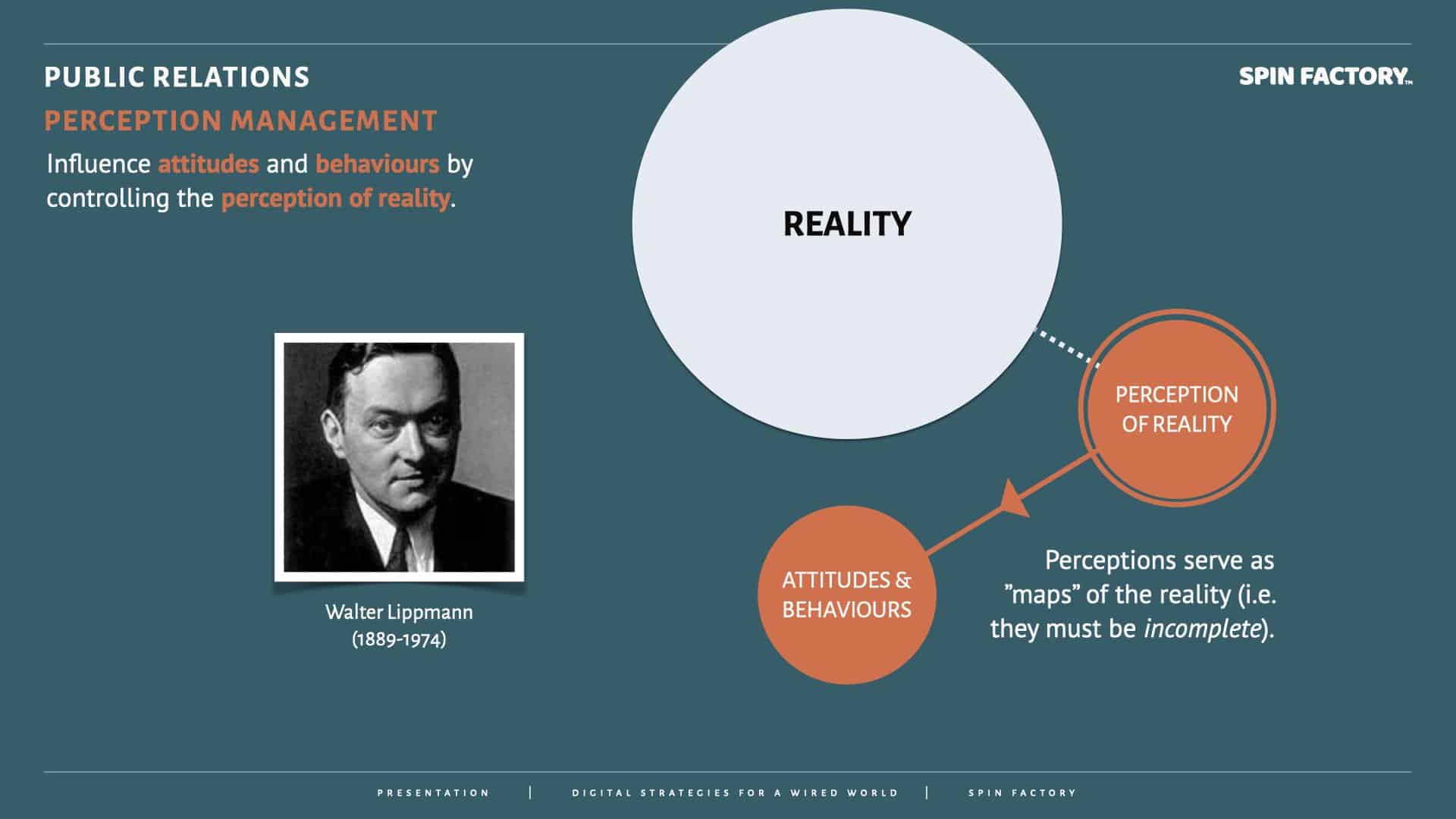
Walter Lippmann and Perception Management
In his seminal work Public Opinion (1922), Walter Lippmann laid the intellectual groundwork for the idea that perception and reality are not the same — a core principle of modern perception management. 8Lippmann, Walter. 1960. Public Opinion (1922). New York: Macmillan.
Lippmann argued that:
Lippmann’s ideas resonate deeply with perception management in public relations.
“We are all captives of the picture in our head — our belief that the world we have experienced is the world that really exists.”
— Walter Lippmann (1889 – 1974)
On Creating Pseudo-Environments
Lippmann coined the term “pseudo-environment,” which describes the filtered, biased, and often artificial version of reality presented by the media. He warned that influential elites could exploit this manufactured reality to manipulate public thought and behaviour.
Lippmann was sceptical about the public’s ability to discern reality from the pseudo-environment, which raises ethical concerns:
Perception management is not inherently sinister, but as Lippmann warned, it places immense power in the hands of those controlling the narrative.
In essence, perception management is the applied PR version of Lippmann’s media critique. It acknowledges that facts alone do not win public trust—priming, framing, storytelling, and emotional appeal do.
Learn more: Perception Management
Annotations
| 1 | Lin, W. (2019). Three Modes of Rhetorical Persuasion. Sino-US English Teaching. https://doi.org/10.17265/1539 – 8072⁄2019.03.003 |
|---|---|
| 2 | Modes of persuasion. (2023, September 27). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modes_of_persuasion |
| 3 | Clarkson, J. J., Tormala, Z. L., & Rucker, D. D. (2008). A new look at the consequences of attitude certainty: The amplification hypothesis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(4), 810 – 825. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013192 |
| 4 | Surviving the Storm: Understanding the Nature of Attacks held at Animal Care Expo, 2011 in Orlando, FL. |
| 5 | Silfwer, J. (2017, June 13). Conversion Theory — Disproportionate Minority Influence. Doctor Spin | The PR Blog. https://doctorspin.net/conversion-theory/ |
| 6 | Beck (1999): Homogenization, Dehumanization and Demonization. |
| 7 | Cognitive dissonance. (2023, November 20). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_dissonance |
| 8 | Lippmann, Walter. 1960. Public Opinion (1922). New York: Macmillan. |