Echo chambers threaten informed, rational debate.
“Algorithmic fragmentation” could long-term undermine the democratic process, as our societies slowly lose their ability to allow informed, rational debates based on a shared understanding of reality.
What do we know about echo chambers?
Here we go:
Echo Chambers on Digital Platforms
Echo chambers, amplified by confirmation bias and media logic, pose a significant societal problem. They create environments where individuals are exposed primarily to opinions and information that reinforce their existing beliefs, leading to a narrow, often distorted worldview.
“Echo chambers in social media contribute to the viral spread of misinformation by acting as initial bandwagons for complex contagions.”
Source: PLoS ONE 1Törnberg, P. (2018). Echo chambers and viral misinformation: Modeling fake news as complex contagion. PLoS ONE, 13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203958
In echo chambers, critical thinking and exposure to diverse perspectives are limited, which can contribute to spreading misinformation and entrenching extremist views. 2Silfwer, J. (2018, August 6). How To Fight Populism. Doctor Spin | The PR Blog. https://doctorspin.net/how-to-fight-populism/
“Echo chambers are not just spaces where opinions are excluded, but also spaces where beliefs are reinforced, contributing to misinformation and collaborative resistance.”
Source: Episteme 3Elzinga, B. (2020). Echo Chambers and Audio Signal Processing. Episteme, 19, 373 — 393. https://doi.org/10.1017/epi.2020.33
Such isolation can intensify ideological polarisation, diminishing the opportunity for constructive dialogue and understanding between different groups.
Echo chambers can undermine the democratic process by creating fragmented publics, each with its own ‘facts’ and interpretations, making consensus and collaborative problem-solving increasingly challenging.
“Echo chambers and epistemic bubbles are distinct social epistemic phenomena, and addressing them requires distinct interventions.”
Source: Episteme 4Nguyen, C. (2018). ECHO CHAMBERS AND EPISTEMIC BUBBLES. Episteme, 17, 141 — 161. https://doi.org/10.1017/epi.2018.32
Learn more: Echo Chambers: Algorithmic Confirmation Bias
Bandwagons for Fake News
Echo chambers on social platforms present a complex challenge in today’s interconnected world. These echo chambers occur when individuals are exposed primarily to viewpoints and information that align with and reinforce their existing beliefs, leading to a homogenised and often distorted perception of reality.
This phenomenon is exacerbated by confirmation bias, where users selectively consume content that confirms their preconceptions, further entrenching their views. These echo chambers can act as catalysts for the viral spread of misinformation, effectively serving as “initial bandwagons” for complex contagions of fake news.
As these echo chambers limit exposure to diverse perspectives and critical thinking, they become fertile grounds for misinformation and the growth of extremist ideologies. The amplification of specific viewpoints at the expense of others not only narrows the spectrum of discourse but also contributes to the polarisation of society, creating divisions that are hard to bridge.
Echo Chambers and Algorithms
The role of social media algorithms in creating and sustaining echo chambers is significant. Social media platforms use sophisticated algorithms to curate and present content based on user preferences, behaviours, and interactions.
These algorithms are designed to maximise engagement, often by showing users content most likely resonates with them. While this can create a more personalised and engaging user experience, it also inadvertently reinforces echo chambers.
As users engage with certain types of content, the algorithms feed them more of the same, creating a feedback loop that further isolates users in their ideological bubbles. This process limits the diversity of content presented to users and makes it challenging for them to encounter information that challenges their viewpoints.
The effect is a digital environment where beliefs are unchallenged and actively reinforced, contributing to collective resistance to alternative perspectives and fostering misinformation.
Undermining a Rational Debate
The implications of echo chambers and algorithm-driven content curation are far-reaching, particularly in the context of democratic processes and societal cohesion. Echo chambers are distinct phenomena that require different interventions.
Echo chambers can fragment publics into separate groups, each with its own set of ‘facts’ and interpretations, making it increasingly difficult to engage in collaborative problem-solving. This fragmentation poses a threat to the democratic process, as it undermines the ability of a society to have informed, rational debates based on a shared understanding of reality.
Addressing the challenges posed by echo chambers and the role of algorithms in their perpetuation is essential for fostering informed, inclusive, and critically engaged publics. It requires awareness and concerted efforts by individuals, social media platforms, news organisations, and policymakers to promote exposure to diverse viewpoints (not just differences in physical appearances) and encourage critical thinking in this wired world of ours.
Confirmation Bias in the Media
Cognitive bias in the media presents a significant issue because it can skew the presentation and interpretation of news, leading to a distorted understanding of events and issues among the public.
“Confirmation bias, the tendency to consume news that confirms pre-existing attitudes and beliefs, can contribute to the spread of false news on digital platforms.”
Source: Digital Journalism 5Ling, R. (2020). Confirmation Bias in the Era of Mobile News Consumption: The Social and Psychological Dimensions. Digital Journalism, 8, 596 — … Continue reading
When media content is influenced by biases — such as confirmation bias, sensationalism, or media logic — it tends to favour certain narratives or perspectives, often at the expense of a balanced and comprehensive view.
This selective representation can reinforce pre-existing beliefs among audiences, contributing to the polarization of public opinion. It also hampers critical thinking, as people are less exposed to diverse viewpoints and more likely to accept biased information as truth.
“Confirmation bias is a cognitive bias in which individuals tend to focus on information that supports their existing beliefs, while overlooking contradictory information.”
Source: Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning 6Barry, P., & Tribe, L. (2009). Confirmation bias. Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/978 – 1‑4419 – 1428-6_2086
Confirmation bias in media reporting can perpetuate stereotypes and misinformation, influencing public opinion and policy decisions based on incomplete or skewed information.
In an era where media plays a crucial role in shaping societal discourse, cognitive biases undermine the credibility and trustworthiness of media outlets. It poses a broader challenge to informed decision-making and democratic processes in society.
Confirmation bias, amplified by social media algorithms and media logic, segregates online communities into isolated information bubbles — echo chambers.
Learn more: Confirmation Bias in Media: The Echo Chamber Challenge
The Media Polarisation Model
We often hear how the media climate is “polarised” — a known and reasonably well-understood effect of classic media logic.
It also seems true that social media logic has amplified the effects of polarisation by grouping people into echo chambers where confirmation bias, conversion theory, and the hostile media effect are allowed to roam freely without any checks and balances.
“Political elites, partisan media, and social media contribute to societal-level political polarization, leading to misperceptions of division among the electorate and fueling animosity and actual ideological polarization over time.”
Source: Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 7Wilson, A., Parker, V., & Feinberg, M. (2020). Polarization in the contemporary political and media landscape. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 34, 223 – 228. … Continue reading
More profoundly, media polarisation is problematic because it draws false lines between extremes that aren’t necessarily perpendicular. These “false lines” will force otherwise balanced media consumers to place themselves between the media-suggested extremes.
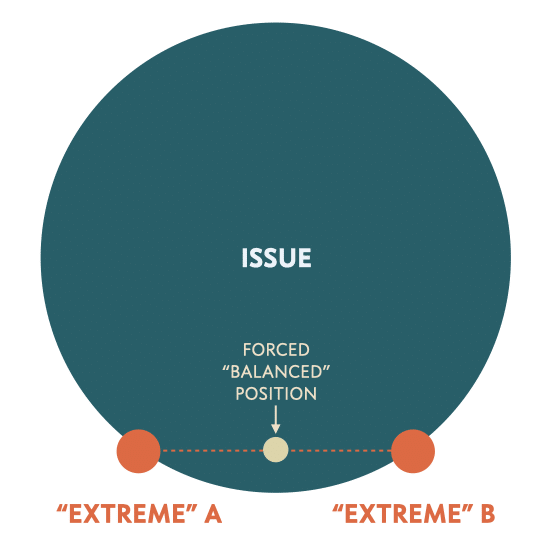
At the extremes, sheltered by the social safety of a like-minded peer group (i.e. echo chamber), it’s possible to disregard opposing evidence as “attacks” on their position. As the amplification hypothesis states, any such attacks will only strengthen the position of the extremes.
The harder you attack someone verbally, the more you convince them of their belief, not yours.
The Post-Truth Zone
The amplification hypothesis sustains a post-truth zone at the extremes through media polarisation. If a) the zone is wide enough and b) the extremes are sufficiently close to each other, the forced “balanced” position between them will also result in the post-truth zone.
“Post-truth is a societal phenomenon, influenced by the expectation that honesty is the default position, and the public tolerance of inaccurate and undefended allegations in politics.”
Source: Nature 8Higgins, K. (2016). Post-truth: a guide for the perplexed. Nature, 540, 9 – 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/540009a
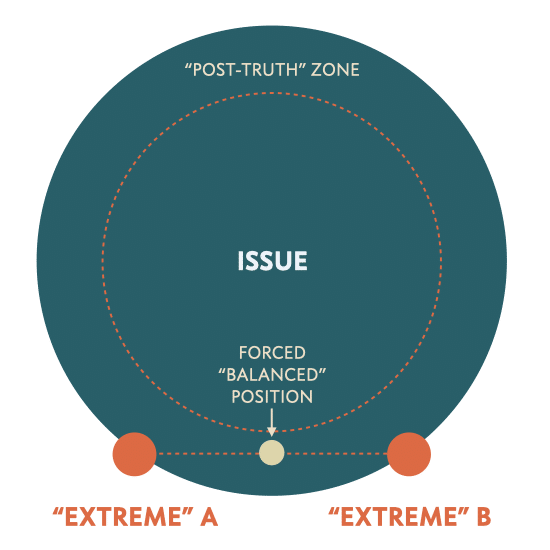
Since the forced “balanced” position will have a hard time sheltering anyone from our fear of social isolation, the spiral of silence partially explains why extremes are so effective in silencing the majority of otherwise balanced media consumers. 9Silfwer, J. (2020, June 4). The Spiral of Silence. Doctor Spin | The PR Blog. https://doctorspin.net/spiral-of-silence/
Why Media Polarisation is Disturbing
Like everyone else, I have opinions. However, as a PR professional with 18+ years of experience, I can analyse media issues without siding with any of the extremes.
But no matter how professional my analysis of a current media issue is, I risk blowback from left and right extremes — with no backing from the silent majority.
Many feel compelled by the news media to choose between outlandish extremes — or settle for an equally outlandish middle ground.
Media trends tend to be cyclical, and I estimate that the post-truth era peaked in 2019. My hope, however, is that the pandemic, followed by global inflation and AI progress, will dampen the media’s interest in extreme positions and shrink the width of the post-truth zone.
“Post-truth communication has shaped our understanding of truth, politics, and the media, with its impact on public policy, history, and social media.”
Source: Social Studies of Science 10Sismondo, S. (2017). Post-truth? Social Studies of Science, 47, 3 — 6. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312717692076
Still, it’s disturbing that the rational business decision for many academics, professionals, and organisations is to strategically steer clear of topics taken “hostage” by left and right extremists — or for organisations to opt for the media blackout tactic.
Normalise Not Having an Opinion
More often than not, in a post-truth society, having no opinion suddenly seems like the only rational escape.

My opinion?
Let’s normalise not having one.
The iron prescription (mental model). Senior advisor Charlie Munger argued: “I have what I call an ‘iron prescription’ that helps me keep sane when I naturally drift toward preferring one ideology over another. I feel that I’m not entitled to have an opinion unless I can state the arguments against my position better than the people who are in opposition. I think that I am qualified to speak only when I’ve reached that state” (Knodell, 2016). 11Knodell, P. A. (2016). All I want to know is where I’m going to die so I’ll never go there: Buffett & Munger – A study in simplicity and uncommon, common sense. PAK Publishing.
Learn more: The Media Polarisation Model

THANKS FOR READING.
Need PR help? Hire me here.

What should you study next?
Spin Academy | Online PR Courses

Spin’s PR School: Free Media PR Course
Elevate your public relations skills with this free Media PR Course—a must-have resource for all aspiring public relations professionals. Boost your career now!
Media Theory
Media Logic
Journalism
Digital Media
Learn more: All Free PR Courses
💡 Subscribe and get a free ebook on how to get better PR.

Annotations
| 1 | Törnberg, P. (2018). Echo chambers and viral misinformation: Modeling fake news as complex contagion. PLoS ONE, 13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203958 |
|---|---|
| 2 | Silfwer, J. (2018, August 6). How To Fight Populism. Doctor Spin | The PR Blog. https://doctorspin.net/how-to-fight-populism/ |
| 3 | Elzinga, B. (2020). Echo Chambers and Audio Signal Processing. Episteme, 19, 373 — 393. https://doi.org/10.1017/epi.2020.33 |
| 4 | Nguyen, C. (2018). ECHO CHAMBERS AND EPISTEMIC BUBBLES. Episteme, 17, 141 — 161. https://doi.org/10.1017/epi.2018.32 |
| 5 | Ling, R. (2020). Confirmation Bias in the Era of Mobile News Consumption: The Social and Psychological Dimensions. Digital Journalism, 8, 596 — 604. https://doi.org/10.1080/21670811.2020.1766987 |
| 6 | Barry, P., & Tribe, L. (2009). Confirmation bias. Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/978 – 1‑4419 – 1428-6_2086 |
| 7 | Wilson, A., Parker, V., & Feinberg, M. (2020). Polarization in the contemporary political and media landscape. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 34, 223 – 228. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/yqvzc |
| 8 | Higgins, K. (2016). Post-truth: a guide for the perplexed. Nature, 540, 9 – 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/540009a |
| 9 | Silfwer, J. (2020, June 4). The Spiral of Silence. Doctor Spin | The PR Blog. https://doctorspin.net/spiral-of-silence/ |
| 10 | Sismondo, S. (2017). Post-truth? Social Studies of Science, 47, 3 — 6. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312717692076 |
| 11 | Knodell, P. A. (2016). All I want to know is where I’m going to die so I’ll never go there: Buffett & Munger – A study in simplicity and uncommon, common sense. PAK Publishing. |


