Your PR campaign is probably too short.
Many organisations underestimate how long it takes for corporate messaging to propagate through a population.
Information has many opportunities to spread fast and wide throughout online social networks, but the revolution of algorithms has less to do with speed and breadth than many of us think.
Here we go:
The Glory Days of Mass Media
As mass media established dominance in the latter half of the 20th century, editorial publishing was always a weak business model. To mitigate this weakness, the mass media had to rely on various forms of advertising to enable their editorial efforts.
There’s an inherent complexity to this relationship. The mass media audience wasn’t keen on paying enough money for editorial content. Instead, they paid with another valuable form of compensation — their attention.
Of course, editorial outlets had to transform the immense value of mass attention somehow. And there was no shortage of special interests ready to pay for a slice of all that attention:
An organisation, starved of attention, trust, and loyalty, is compelled to wage a perpetual struggle for its continued existence.
So, the audience pays for content with their attention, advertisers pay for attention with their money, and the editorial outlet pays their staff with ad revenue.
In its not-so-modest Madison Avenue beginnings, advertising had considerable strengths as a business model. Given the nature of mass media, huge audiences could be reached at any one time. It’s also reasonable to argue that traditional advertising had more prominent effects on the audience back then.
It was a great time to advertise.
And PR was allowed to piggyback.
But nothing lasts forever.
The Advent of Network Propagation
Now, most of us have some sense of how events unfolded. With the advent of the digital era, our media landscape underwent a fundamental transformation. Anyone stuck in traditional business models dependent on mass media is still struggling to find the right way to negotiate our many new online realities.
In this article, I’d like to direct your attention to such a specific change — network propagation.
The basic communication model describes a) the sender, b) the signal, c) the medium, and d) the receiver. The idea of a considerable time displacement between when the signal is sent and received is not novel; many books are read even millennia after they were first created. But this displacement has rarely been a considerable consideration.
For a long time throughout human history, the time it has taken for signals to propagate throughout a population has exponentially decreased due to ever more efficient means of mediation, from cave paintings and word-of-mouth by the campfire to global mass media conglomerates.
The Power of Signal Propagation Delay
But this is where it gets complicated. With the internet, signals were able to propagate faster than ever before. And anyone, not just mass media conglomerates, could suddenly reach global audiences at light speeds. But at this point, something had to give.
Our mental bandwidth as humans is remarkable, but not without its limits. Also, our brains haven’t exactly evolved in tandem with our means of mediation.
Although rarely discussed in such terms, the solution to the problem of limited mental bandwidth and the explosion of available signals was nothing short of a revolution. Human gatekeepers were replaced with algorithms. For whatever reason, mass media conglomerates refused to implement algorithms, leaving the playing field open to algorithm-driven tech giants like Google (now Alphabet) and Facebook (now Meta).
But this is also where the time displacement between sent and received stopped propagating exponentially. Instead, signal propagation reverted to a time of cave paintings and word-of-mouth by the campfire.
In crude terms, gatekeepers had the power to sort messages but lacked the technology to send signals at points in time determined by receivers individually. The marvel of algorithms is, contrary to popular belief, not their ability to sort signals. Their revolutionary prowess stems from their ability to delay messages throughout social graphs. 1Signal propagation delay. (2023, April 13). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_propagation_delay
Propagating Faster — and Slower
For a long time, signals were continuously spreading faster to larger audiences. At the algorithmic break, signals have learnt to wait patiently at nodes in a network before moving along. Today, signals can sometimes move fast, sometimes slow — and pass various socially constructed filters, allowing an often uncanny targeting precision.
Even the algorithms themselves have undergone various evolutions (such as the silent shift). But their networked nature establishes new rules for successfully propagating targeted signals.
What does the time displacement of network propagation mean for public relations and marketing? Well, for one thing — your campaigns are probably too short today.
It’s a non-sequitur to say that signals must propagate faster or slower today. A more precise way of thinking of network propagation through online social networks of algorithms is to realise that signals are getting more efficient at taking the time they need to propagate.
A Humility Check for Your PR Campaign
For corporate communications and marketing, this should be a humility check. A press release or an ad might be significant to a specific audience. In a wired world, such signals stand a good chance of reaching their recipients eventually. How long this takes will be dictated by individual needs that might not fit with ambitious corporate timelines.
The outcome is straightforward:
Most PR campaigns today are way too short. They’re created based on the sender’s needs in a media landscape where propagation is entirely dictated by the recipients’ needs.
Yes, the internet is “fast.” But relationships take time to build. It takes time to shift perceptions. Individual audience members will only process your corporate messaging if or when they need them. And our brains have limited bandwidths.
Despite the instantaneity of modern information technologies, cultivating human relationships remains firmly anchored in the unhurried passage of time.
Brands must be patient and have the structural fortitude to stay consistent for their PR messaging to propagate properly and thoroughly before jumping onto the next PR campaign.
Don’t go for a huge splash tomorrow.
Go for over-the-top relevancy day-in and day-out.
The Silent Switch
All social media algorithms are built differently and are constantly being developed. At the same time, social media users’ behaviours are evolving.
Still, there was a way that social media algorithms used to behave—and there is a way that social media algorithms behave now.
This has been a fundamental but silent switch.
How Social Media Algorithms Used To Behave
For more than a decade, social media algorithms would deliver organic reach according to a distribution that looked something like this:
This distribution of organic reach enabled organisations to use social media despite not being “media companies.”
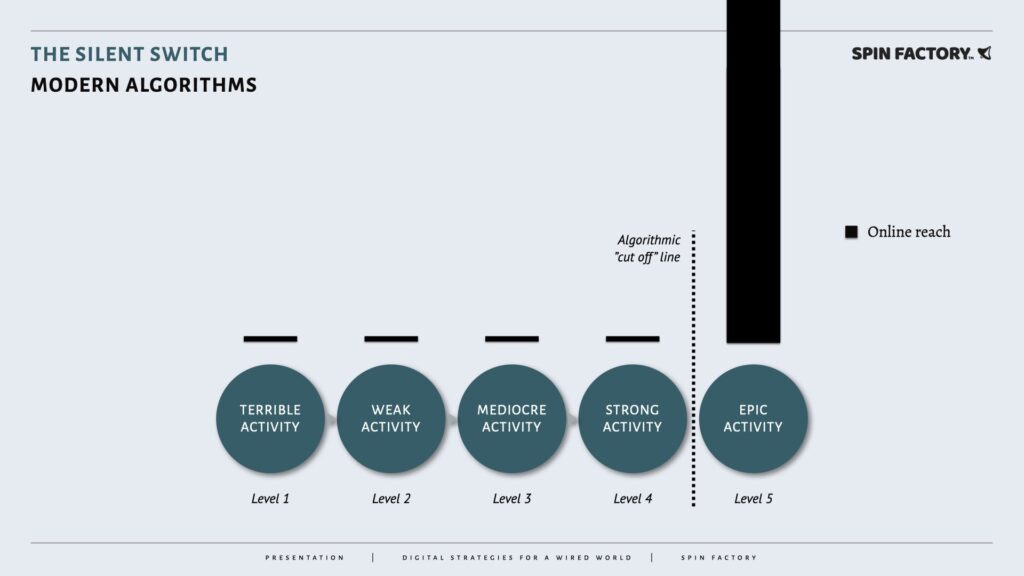
How Social Media Algorithms Behave Today
Today, after the silent shift, social media algorithms deliver organic reach more like this:
The increased competition and sophistication among content creators partially explain this new type of distribution. However, going viral is still just as possible for anyone.
How does this work?
The Single Content Algorithm
How can a social network predict what users will like?
Content from a trusted creator trusted by a large community of followers used to be the leading indicator of future performance. But today, social networks have found a better way to predict content success.
The single content algorithm = when social networks demote content creator authority to promote single content performance to maximise user engagement for ad revenue.
The single content algorithm presents newly published content to a limited audience sample size:
If the newly published content tests successfully, the social media algorithm pushes that content to a slightly larger statistical subset. And so on.
This iterative process means that single pieces of content worthy of going viral will go viral, a) even if it takes a longer time, and b) regardless of the content creator’s number of followers.
Learn more: The Silent Switch

THANKS FOR READING.
Need PR help? Hire me here.

Annotations
| 1 | Signal propagation delay. (2023, April 13). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_propagation_delay |
|---|