What can we learn from the content attention pyramid?.
There’s no “standing still” in social media publishing. If you stand still and neglect the need for constant evolution, you’ll slowly start to sink into the content abyss — perhaps never to be seen again.
Either you manage to stay afloat, or you find an arena where you’re able to compete successfully. Everything else is futile.
Here we go:
The Content Attention Pyramid (CAP)
Each content niche has a limited amount of available attention; in other words, there is never enough mental bandwidth to cover all digital content.
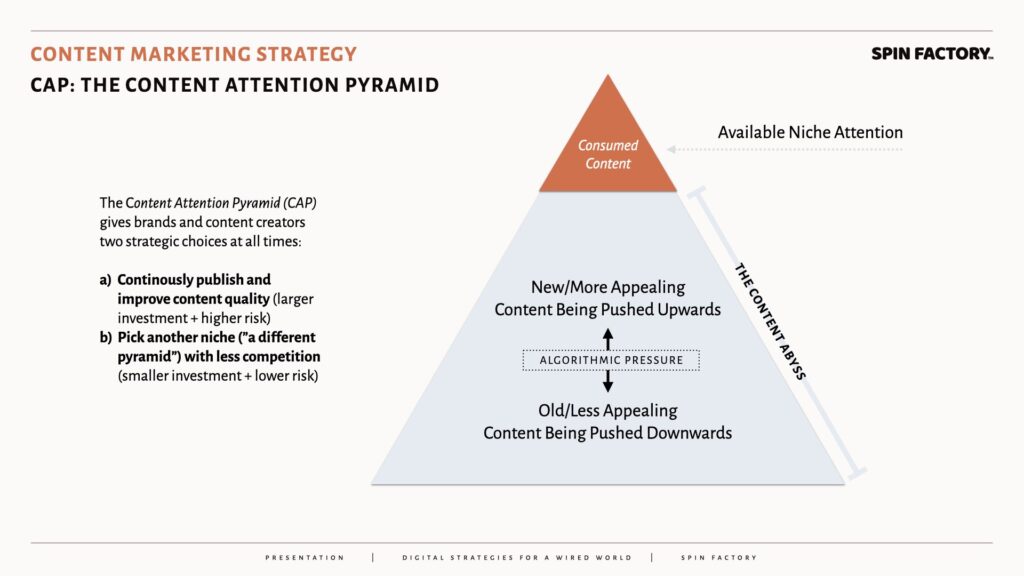
Social media algorithms take cues from social interaction data and various forms of analysis to satisfy the need for information, but also, and more importantly, do away with content that is no longer needed — or perhaps it never was.
At any given moment in time, brands and content creators face two strategic choices:
Failing to adhere to both of these choices, the brand or the content creator will find themselves slowly sinking into the content abyss — until their newly published content goes directly into the void, only to stay there, forever.
Learn more: The Social Media Attention Pyramid
The Anatomy of Attention
Attention is an essential component of public relations:
An organisation, starved of attention, trust, and loyalty, is compelled to wage a perpetual struggle for its continued existence.
And it’s not just organisations. We all seem to crave attention in some form or another:
“People want to be loved; failing that admired; failing that feared; failing that hated and despised. They want to evoke some sort of sentiment. The soul shudders before oblivion and seeks connection at any price.”
— Hjalmar Söderberg (1869−1941), Swedish author
It’s fear of social isolation—and attention starvation.
Types of Attention
But what constitutes ‘attention’?
“Attention is a complex, real neural architecture (‘RNA’) model that integrates various cognitive models and brain centers to perform tasks like visual search.”
Source: Trends in cognitive sciences 1Shipp, S. (2004). The brain circuitry of attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 223 – 230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2004.03.004
Each of the below terms refers to a specific aspect or type of attention (“mental bandwidth”), a complex cognitive process. 2Schweizer, K., Moosbrugger, H., & Goldhammer, F. (2005). The structure of the relationship between attention and intelligence. Intelligence, 33(6), 589 – 611. … Continue reading
Let’s explore different types of attention:
Each type of attention is likely to play a role in how we interact with and process information from our environment, and understanding these different aspects is key in fields like psychology, neuroscience, and education.
Learn more: The Anatomy of Attention

THANKS FOR READING.
Need PR help? Hire me here.

Annotations
| 1 | Shipp, S. (2004). The brain circuitry of attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 223 – 230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2004.03.004 |
|---|---|
| 2 | Schweizer, K., Moosbrugger, H., & Goldhammer, F. (2005). The structure of the relationship between attention and intelligence. Intelligence, 33(6), 589 – 611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2005.07.001 |


